
Nerve compression in this area is uncommon, but is sometimes caused by a laterally herniated disc.Īt these four levels there can be a lot of overlap of pathology.įor instance a herniated disc can cause nerve compression at the level of the disc, but also at the level of the foramen or extra-foraminal when there is migration of the disc. were most highly associated with end - plate irregularities and disc bulging. Narrowing of the foramen is seen in facet arthrosis, spondylolisthesis and foraminal disc herniation - usually a migrated disc from a lower level. Or is the clinical picture complex, for example, in a situation in. This is the area between two pedicles, where the nerve leaves the spinal canal. Narrowing of the lateral recess is caused by facet arthrosis, usually in combination with hypertrophy of the flavum ligament and bulging of the disc. This is the area below the disc where the nerve runs more laterally towards the foramen. Mostly by herniated discs and less frequently due to spinal stenosis. Both bulging and herniated discs usually remain asymptomatic however, they can cause discomfort and disability in various parts of the body if the disc. This is the most common area where nerves are compressed. It follows from this discussion that the clinical picture of a patient. In patients with symptoms of nerve root compression, there are four levels that need to be studied: with resultant ischemia of the cord, or by a herniated intervertebral disc. When a disc in your lower spine bulges or tears, you may feel pain in your lower back and/or your leg. White Matter Lesions - Differential diagnosis.
IPICTURE OF BULGING DISC ON SPINE HOW TO
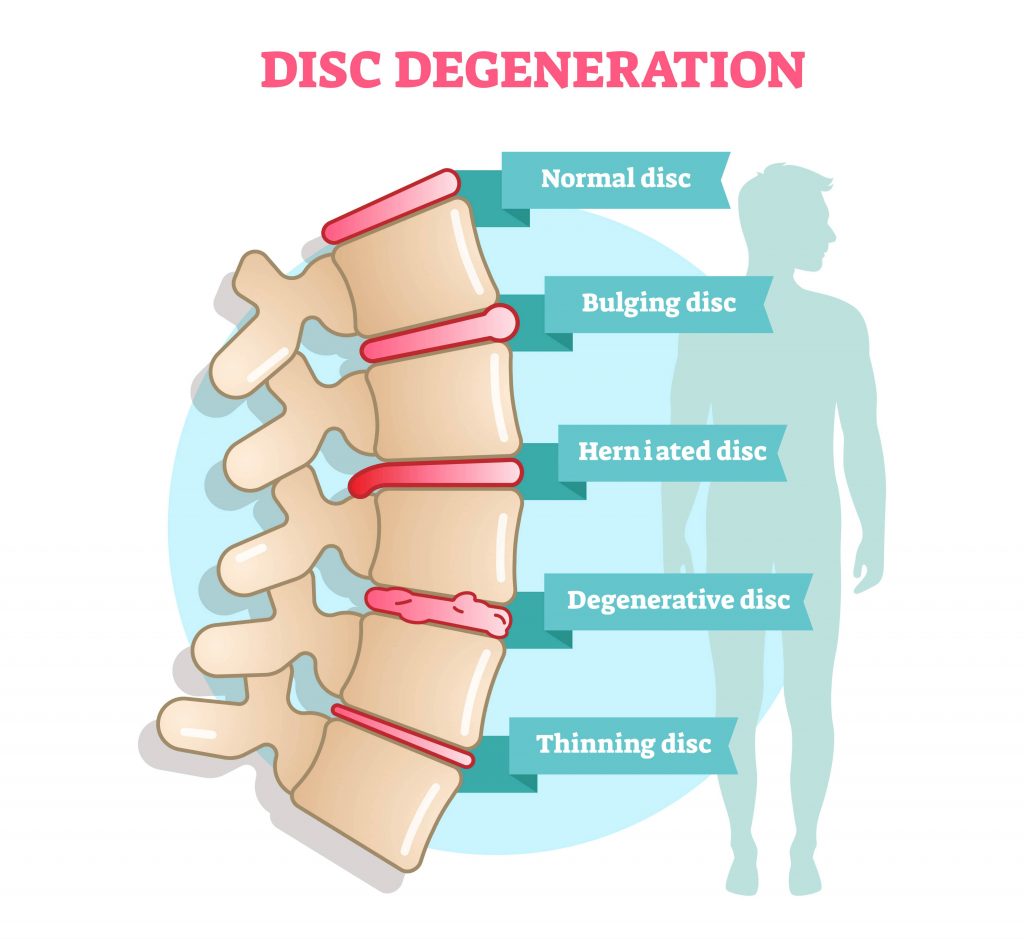
How to Differentiate Carotid Obstructions.Disc degeneration, bulging disks, and herniated discs occur very commonly. TI-RADS - Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System The two most common slices that we look at on MRI scans of the spine are the.Esophagus II: Strictures, Acute syndromes, Neoplasms and Vascular impressions.70 percent of these people had either bulging or herniated discs. Esophagus I: anatomy, rings, inflammation Your herniated disc, your arthritis, your meniscal tear - your very own bashed - in.Vascular Anomalies of Aorta, Pulmonary and Systemic vessels A disc made of a gel-like material (nucleus pulposus) surrounded by a thick fibrous ring (annulus fibrosus) is situated between the vertebral bodies of L5 and S1.Bulge is a term for an image and can be a normal variant (usually at L5-S1). Contrast-enhanced MRA of peripheral vessels In simple terms, a disc bulge refers to an apparent generalized extension of disc tissues beyond the edges of the edge of vertebrae, usually less than 3mm.While the pressure on your nerves and spine could be caused by other conditions, it will help your doctor determine if you have compression on your nerves. Ischemic and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy The doctor can use an X-ray to look for pressure on your nerves and spine by injecting a dye into your body.Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System 2.0.Bi-RADS for Mammography and Ultrasound 2013.Transvaginal Ultrasound for Non-Gynaecological Conditions.Acute Abdomen in Gynaecology - Ultrasound.Appendicitis - Pitfalls in US and CT diagnosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
